The Rise of Humanoid Robots in Warehouses
Introduction to Humanoid Robots in Logistics
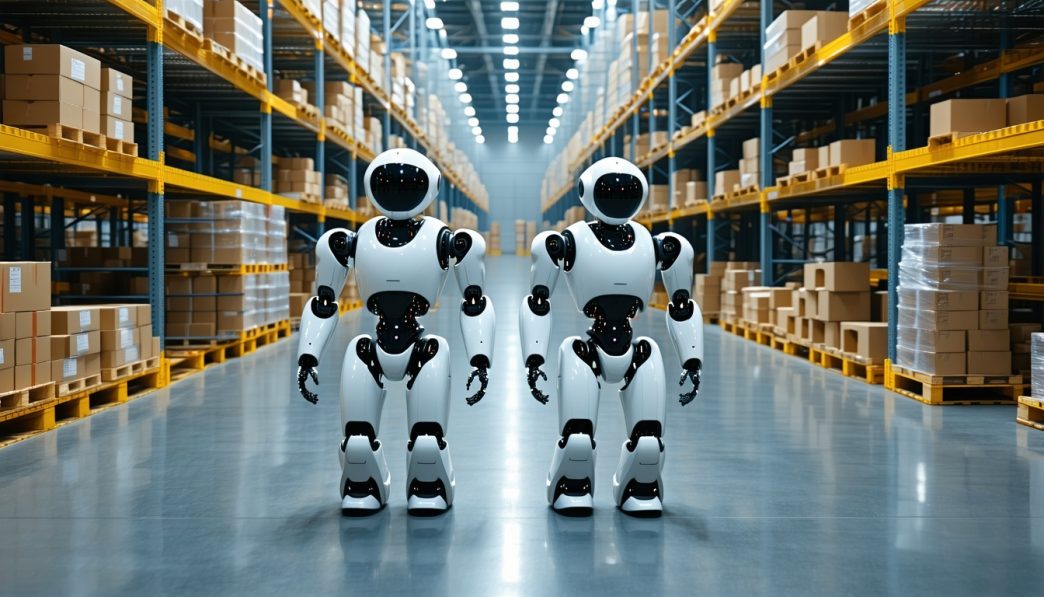
The integration of humanoid robots into logistics and warehouse operations has marked a significant shift in how goods are handled and processed. These robots are designed to replicate human movements and tasks, which makes them adaptable to various roles in the supply chain. With the growing demand for efficiency and productivity, businesses are increasingly turning to humanoid robots to optimize their workflows.
Evolution of Technology in Warehouse Operations
Over the past few decades, technology in warehouse operations has evolved dramatically. Initially, automation involved simple conveyors and sorting systems. Now, advanced robotics, AI, and machine learning are revolutionizing the industry.
Modern humanoid robots are equipped with state-of-the-art sensors and AI algorithms, allowing them to navigate complex environments and interact with their surroundings. This evolution facilitates more intricate tasks such as picking, packing, and inventory management. The table below highlights key innovations in warehouse technology.
| Year | Technology Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2000 | Introduction of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) |
| 2010 | Use of RFID for inventory tracking |
| 2020 | Launch of AI-driven warehouse management systems |
| 2023 | Deployment of humanoid robots in logistics |
Role of Humanoid Robots in Modern Warehouses
Humanoid robots play a pivotal role in enhancing warehouse efficiency. They can take on various tasks that were once labor-intensive and time-consuming. From lifting heavy objects to accurately sorting packages, these robots streamline operations significantly.
Key functions of humanoid robots in warehouses include:
- Inventory Management: Robots equipped with advanced tracking systems can handle inventory counts and restocking efficiently.
- Order Fulfillment: They assist in picking and packing items, ensuring accuracy in order processing.
- Human-Robot Collaboration: Humanoid robots can work alongside human staff, alleviating their workload and allowing them to focus on more complex tasks.
The implementation of humanoid robots is indicative of a growing trend in the logistics sector towards embracing automation. As the demand for faster and more accurate warehouse operations continues to rise, the role of humanoid robots is anticipated to expand, paving the way for a revolution in logistics. For more insights into humanoid robotics, explore our articles on humanoid robots in healthcare and humanoid robots for education.
Types of Humanoid Robots
Understanding the variety of humanoid robots is essential for recognizing their potential roles in logistics and warehouse operations. This section discusses the characteristics of humanoid robots, along with their applications in warehouses.
Characteristics of Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots are designed with human-like features to perform tasks efficiently. They possess several key characteristics:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Structure | Bipedal design resembling human anatomy, enabling movement through narrow aisles. |
| Sensors | Equipped with various sensors for navigation, object recognition, and environmental awareness. |
| Mobility | Capable of walking, lifting, and carrying items, enhancing versatility in operations. |
| AI Capabilities | Integrated artificial intelligence for decision-making and adapting to new tasks. |
| Communication | Features voice interfaces to interact with employees effectively, enhancing teamwork. |
These characteristics make humanoid robots adaptable for various tasks commonly performed in warehouses.
Applications of Humanoid Robots in Warehouses
Humanoid robots are increasingly utilized in warehouses for multiple applications, enhancing operational efficiency. Some common applications include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Inventory Management | Assisting in tracking, sorting, and managing inventory levels efficiently. |
| Picking and Packing | Performing tasks such as picking items from shelves and packing them for shipping. |
| Sorting and Routing | Sorting products based on destination and efficiently routing them within the warehouse. |
| Last-Mile Delivery | Aiding in the final stages of delivery, bridging gaps between warehouse and customers. |
| Equipment Maintenance | Conducting routine checks and maintenance on warehouse equipment to ensure functionality. |
These applications illustrate the versatility of humanoid robots in logistics. They showcase a transformative potential in warehouse operations, improving productivity and workflow. For insights into different humanoid robotics models, explore our articles on tesla optimus robot and agility digit robot.
Advantages of Humanoid Robots in Warehouse Operations
Humanoid robots offer several key advantages in warehouse operations, significantly enhancing productivity and safety. They are becoming an integral part of logistics due to their efficiency, precision, and ability to mitigate risks in the working environment.
Efficiency and Speed
Humanoid robots excel in performing repetitive tasks at a remarkable pace. Their ability to operate continuously without rest leads to increased output and faster processing times. This enhanced speed helps warehouses maintain higher throughput levels, ensuring timely deliveries and inventory management.
| Task Type | Time Taken by Human (min) | Time Taken by Humanoid Robot (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Sorting Packages | 15 | 5 |
| Inventory Checks | 30 | 10 |
| Loading and Unloading | 20 | 8 |
Precision and Accuracy
In warehouse settings, precision in tasks such as inventory management and order fulfillment is critical. Humanoid robots utilize advanced algorithms and sensors to execute tasks with high accuracy. Their ability to consistently handle items correctly reduces errors in picking and packing, thus minimizing costly mistakes.
| Accuracy Improvement | Before Humanoid Robots (%) | After Humanoid Robots (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Accuracy | 85 | 98 |
| Order Fulfillment Rate | 90 | 99 |
Safety and Risk Mitigation
Safety is a paramount concern in warehouse environments, where heavy lifting and hazardous equipment are commonplace. Humanoid robots can take on physically demanding tasks, reducing the risk of injuries to human workers. Furthermore, they are equipped with safety systems and sensors that enable them to navigate complex environments while avoiding accidents.
| Safety Incident Reduction | Before Humanoid Robots | After Humanoid Robots |
|---|---|---|
| Accident Rate per 1000 hours | 10 | 2 |
| Injury Rate per 100 employees | 5 | 1 |
Integrating humanoid robots in logistics presents a multitude of benefits that enhance operational workflows. Their contributions in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and safety make them valuable assets in modern warehouse environments. For more insights on these topics, consider exploring the role of humanoid robots in logistics.
Challenges and Considerations
The integration of humanoid robots into warehouse operations poses several challenges that need to be carefully considered. This section outlines key aspects such as system integration, costs associated with implementation, and the ethical implications of deploying humanoid robots in logistics.
Integration with Existing Systems
Proper integration of humanoid robots into existing warehouse systems is a critical hurdle. Many warehouses utilize advanced technology and established workflows. Ensuring that new robotic systems communicate seamlessly with pre-existing software and hardware is essential for efficiency.
| Integration Aspect | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Compatibility | Humanoid robots must work with existing inventory management systems. |
| Communication | Robots need to relay information to warehouse management software. |
| Training | Staff requires training to work alongside humanoid robots effectively. |
Warehouse managers must assess the compatibility and functionality of humanoid robots with their current systems. This includes understanding data exchange standards and ensuring robots can correctly interpret the workflows.
Cost and Maintenance
The financial investment for humanoid robots can be substantial. Costs include not only the initial purchase but also ongoing maintenance and operational expenses. Organizations must evaluate the return on investment (ROI) when adopting this technology.
| Cost Type | Estimation |
|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Robotics systems can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars. |
| Maintenance Costs | Regular servicing may add additional expenses annually. |
| Staff Training | Investing in employee training is crucial for proper usage and safety. |
Maintenance is crucial for ensuring longevity and performance. A comprehensive maintenance plan, including software updates and hardware servicing, is necessary to realize the full capabilities of humanoid robots.
Ethical and Social Implications
The introduction of humanoid robots brings forward various ethical and social considerations. Questions arise regarding job displacement, privacy, and the treatment of robots in the workplace. It is vital for organizations to address these concerns proactively.
| Ethical Aspect | Discussion Points |
|---|---|
| Job Displacement | Will robots replace human jobs or lead to new roles? |
| Safety Concerns | How do companies ensure the safety of human workers alongside robots? |
| Privacy Issues | What data do robots collect, and how is it used? |
A thoughtful approach is needed to navigate these ethical concerns. Organizations should consider creating policies that promote collaborative working environments between humans and robots, while also ensuring transparency in data handling practices.
By acknowledging and addressing these challenges, businesses can better prepare for the successful integration of humanoid robots in logistics, enhancing warehouse operations while safeguarding employee welfare.
Case Studies
Success Stories of Humanoid Robots in Warehousing
Numerous enterprises have successfully integrated humanoid robots into their warehouse operations. These implementations have showcased significant advancements in efficiency and productivity. Below are examples highlighting the success of humanoid robots in logistics environments.
| Company | Robot Model | Implemented Tasks | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Retailer A | Agility Digit Robot | Inventory management, picking orders | 30% increase in order fulfillment speed |
| E-commerce Company B | Xiaomi CyberOne | Sorting and packing | 25% reduction in labor costs |
| Distribution Center C | Sanctuary AI Phoenix | Shelf restocking and customer assistance | Improved customer satisfaction ratings by 20% |
These success stories illustrate the capabilities of humanoid robots in facilitating warehouse tasks, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency.
Lessons Learned from Implementations
While the integration of humanoid robots has proven beneficial, several lessons have emerged from these implementations:
-
Training and Adaptation: Employees must be prepared to interact with humanoid robots. Training programs that include robotic operation and maintenance are essential for effective collaboration.
-
Systems Integration: Successful implementations require a seamless integration of robotic systems with existing warehouse management systems. Companies have learned the importance of compatibility and real-time data synchronization.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Regular evaluations of robotic performance reveal essential insights for improvement. Continual adjustments in processes and tasks can maximize the effectiveness of humanoid robots.
-
Feedback Mechanism: Collecting feedback from human workers regarding the interaction with humanoid robots helps optimize task delegation. This feedback can lead to enhancements in robot programming and functionality.
These insights serve as a foundation for future projects involving humanoid robots in logistics, ensuring organizations can maximize their return on investment and improve overall operations. For further exploration of the role of humanoid robots in the logistics industry, consider reviewing our piece on humanoid robots in logistics.
Future Outlook
As humanoid robots continue to advance, various potential innovations are expected to enhance their capabilities in logistics. These advancements aim to improve their efficiency, adaptability, and integration within warehouse environments.
Potential Innovations in Humanoid Robotics
Innovations in humanoid robotics can be categorized into several key areas, including mobility, autonomy, and human-robot interaction.
| Innovation Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Advanced Navigation Systems | Enhancements in sensors and AI algorithms support robots in navigating complex environments, allowing for safer and more efficient operations. |
| Enhanced AI Capabilities | Continued development of AI models enables robots to learn from their environments and adapt to new tasks autonomously. |
| Improved Emotional Intelligence | Robots equipped with emotion recognition technology can respond to human interactions more effectively, making them more relatable and approachable in the workplace. |
| Smart Charging Solutions | Innovations in charging technologies, such as automated docking stations, reduce downtime and increase operational efficiency. |
| Collaboration Software | Development of user-friendly software platforms facilitates easier integration and communication between robots and human workers. |
For more insights into technological advancements, readers might explore humanoid robot sensors or ai models in humanoid robots.
Impact on the Future of Warehouse Operations
The integration of humanoid robots in logistics is expected to reshape warehouse operations significantly. Increased efficiency and accuracy can lead to substantial cost savings and productivity improvements. Additionally, humanoid robots may help address labor shortages by performing repetitive or hazardous tasks.
Consider the following potential impacts:
| Impact Area | Expected Changes |
|---|---|
| Labor Dynamics | Robots will assist or supplement human workers, altering workforce structures and responsibilities. |
| Productivity Levels | Enhanced speed and precision in handling goods may lead to greater throughput and reduced delivery times. |
| Safety Enhancements | With robots managing dangerous tasks, workplace accidents may decrease, fostering a safer work environment. |
| Customization and Flexibility | Humanoid robots can be programmed for various warehouse functions, allowing for dynamic adjustments based on operational needs. |
Through the ongoing advancement of humanoid robots in logistics, companies will likely find innovative solutions to address existing challenges. Strategies for integrating these robots may vary, offering unique benefits tailored to individual warehouse needs. For additional contextual information, see our articles on humanoid robots for home use and humanoid robots vs AI assistants.